 |
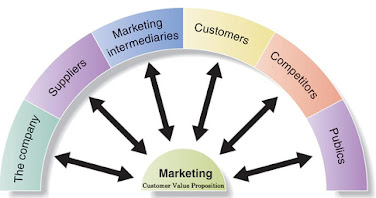
| The Company's Microenvironment |
The Company
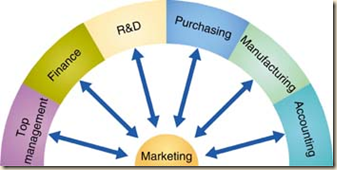
In designing marketing plans, marketing management should take other company groups, such as top management, finance, research and development (R & D), purchasing, manufacturing, and accounting, into consideration. All these interrelated groups form the internal environment.
Top management sets the company's mission, objectives, broad strategies, and policies. Marketing managers must make decisions consistent with the plans made by top management, and marketing plans must be approved by top management before they can be implemented. Marketing managers must also work closely with other company departments. Finance is concerned with finding and using funds to carry out the marketing plan. The R & D department focuses on the problems of designing safe and attractive products. Purchasing worries about getting supplies and materials, whereas manufacturing is responsible for producing the desired quality and quantity of products. Accounting has to measure revenues and costs to help marketers know how well it is achieving its objectives. Therefore, all of these departments impact the marketing department's plans and actions. Under the marketing concept, all of these functions must 'think customer' and they should work together to provide superior customer value and satisfaction.
Suppliers
Suppliers are an important link in the
company's overall customer 'value delivery system". They provide the
resources needed by the company to produce its goods and services. Supplier
developments can seriously affect marketing. Marketing managers must watch
supply availability - supply shortages or delays, labor strikes, and other
events can cost sales in the short run and damage customers [Satisfaction in the
long run. Marketing managers must also monitor the price trends of their key
inputs. Rising supply costs may force price increases that can harm the
company's sales volume.
Marketing Intermediaries
Marketing intermediaries are firms that
help the company to promote, sell and distribute its goods to final buyers.
They include resellers, physical distribution firms, marketing services
agencies, and financial intermediaries. Resellers are distribution channel firms
that help the company find customers or make sales to them). These include
wholesalers and retailers which buy and resell the merchandise. Selecting and
working with resellers is not easy. No longer do manufacturers have many small,
independent resellers from which to choose. They now face large and growing
reseller organizations. These organizations frequently have enough power to
dictate terms or even shut the manufacturer out of large markets.
Physical distribution firms help the
company to stock and move goods from their points of origin to their
destinations. Working with warehouse and transportation firms, a company must
determine the best ways to store and ship goods, balancing such factors as
cost, delivery, speed, and safety. Marketing services agencies are the marketing
research firms, advertising agencies, media firms, and marketing consultancies
that help the company target and promote its products to the right markets.
When the company decides to use one of these agencies, it must choose carefully
because the firms vary in creativity, quality, service, and price. The company
has to review the performance of these firms regularly and consider replacing
those that no longer perform well. Financial intermediaries include banks,
credit companies, insurance companies, and other businesses that help finance
transactions or insure against the risks associated with the buying and selling
of goods. Most firms and customers depend on financial intermediaries to
finance their transactions. The company's marketing performance can be
seriously affected by rising credit costs and limited credit. For example,
small and medium-sized businesses in the United Kingdom have often found
difficulty in obtaining finance for market and product development activities.
Many such businesses blame this on the unsupportive financial system in the UK.
In marked contrast, the Japanese keiretsu system favors lower-cost financing
for both large and small companies that form part of the informal network of
banking, trading, and commercial organizations within the Itieretsu, Whether or
not businesses enjoy the support of a favorable financial system, individual
businesses must be aware of financial organizations' impact on marketing
effectiveness. For this reason, the company has to develop strong relationships
with the most important financial institutions. Like suppliers, marketing
intermediaries form an important component of the company's overall value
delivery system. In its quest to create satisfying customer relationships, the
company must do more than just optimize its own performance. It must partner
effectively with suppliers and marketing intermediaries to optimize the
performance of the entire system
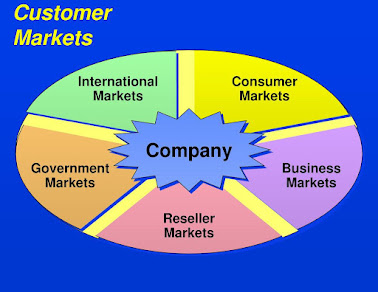
Customers
The company must study its customer markets closely. Consumer markets consist of individuals and households that buy goods and services for personal consumption. Business markets buy goods and services for further processing or for use in their production process, whereas reseller markets buy goods and services to resell at a profit. Institutional markets are made up of schools, hospitals, nursing homes, prisons, and other institutions that provide goods and services to people in their care.
Government markets are made up of government
agencies that buy goods and services in order to produce public services or
transfer the goods and services to others who need them. Finally, international
markets consist of buyers in other countries, including consumers, producers,
resellers, and governments. Each market type has special characteristics Chat
calls for careful study by the seller. At any point in time, the firm may deal
with one or more customer markets: for example, Unilever has to communicate
detergent brand benefits to consumers as well as maintain a dialogue with
retailers that stock and resell its branded products.
Competitors
The
marketing concept states that to be successful, a company must provide greater
customer value and satisfaction than its competitors do. Thus, marketers must
do more than simply adapt to the needs of target consumers. They must also gain a strategic advantage by positioning their offerings strongly against
competitors' offerings in the minds of consumers. No single competitive
marketing strategy is best for all companies. Each firm should consider its own
size and industry position compared to those of its competitors. Large firms
with dominant positions in an industry can use certain strategies that smaller
firms cannot afford. But being large is not enough. There are winning
strategies for large firms, but there are also losing ones. And small firms can
develop strategies that give them better rates of return than large firms
enjoy.
( Keywords )



Post a Comment