 |
| What is gout? |
What is gout?
Doctors place gout under the umbrella term
“arthritis” — a broad range of joint diseases and joint
pain. Some forms of arthritis inflame joints, while others don’t. A gout is a
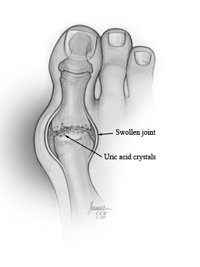
common form of inflammatory arthritis. It’s due to a crystal called uric acid.
Gout causes pain and swelling in one or more joints. It typically affects the big toe. But it’s also found in other joints, including the knee, ankle, foot, hand, wrist, and elbow.
Who is affected by gout?
Gout can affect anyone. It usually occurs
earlier in men than women. It generally occurs after menopause in women. Men can be three times more likely
than women to get it because they have higher levels of uric acid most of their
lives. Women reach these uric acid levels after menopause.
People are more likely to get gout if they
have:
- Obesity, or a lot of extra weight.
- Congestive heart failure.
- Diabetes.
- Family history of gout.
- Hypertension (high blood pressure).
- Kidney disease.
You are also
more likely to develop gout if you:
- Consume a diet high in animal proteins
- Consume a significant amount of alcohol
- Are on water pills (diuretics).
What causes gout?
The human
body makes uric acid during the breakdown of chemicals called purines found in
certain food and drinks. This normal byproduct goes through the kidneys and
exits the body when you pee.
Sometimes the body produces too much uric acid. Or the kidneys can’t do a good job handling it. When the body has high levels of uric acid or hyperuricemia, uric acid crystals can concentrate in the joints. The sharp, needle-like crystals cause gout. However, many people with higher uric acid levels never get gout.
What are the symptoms of gout?
An episode
of gout is called a gout attack. Gout attacks are very painful and can happen
quite suddenly, often overnight. During a gout attack, symptoms in the affected
joint(s) may include:
- Intense pain.
- Redness.
- Stiffness.
- Swelling.
- Tenderness, even
to light touch, such as from a bedsheet.
- Warmth or a
feeling like the joint is “on fire.”
- How long does a
gout attack last?
A gout
attack can last a week or two. Between gout attacks, you may have no symptoms
at all.
How often do gout attacks happen?
Some people have gout attacks frequently,
while others go years between episodes. If gout isn’t treated, attacks may
become more frequent and last longer. Gout attacks can happen over and over
again in the same joint or affect different joints.
How does a doctor diagnose gout?
If you have sudden or severe pain in a
joint, you should talk to your primary care provider (PCP). Your PCP may send you to
a rheumatologist, a doctor who specializes in gout and other kinds of
arthritis.
Healthcare providers consider several
things when confirming gout:
- Symptoms: The provider will ask you to describe your
symptoms, how often they happen, and how long they last.
- Physical examination: Your provider
will examine the affected joint(s) to look for swelling, redness, and
warmth.
- Blood work: A test can measure the amount of uric acid
in your blood.
- Imaging tests: You may have pictures taken of the affected
joint(s) with X-rays, an ultrasound, or an MRI.
- Aspiration: The provider may
use a needle to pull fluid from the joint. Using a microscope, a team
member can look for uric acid crystals (confirming gout) or a different
problem (such as bacteria with infection or other types of crystal).
How is gout treated?
Your healthcare provider may prescribe
certain medications to treat gout.
Some drugs help control symptoms:
- NSAIDs can reduce pain and swelling. Some people
with kidney disease, stomach ulcers, and other health problems cannot take NSAIDs.
- Colchicine can reduce inflammation and pain if
you take it within 24 hours of a gout attack. It’s given by mouth.
- Corticosteroids can relieve pain and swelling.
You take steroids by mouth or with an injection.
Drugs that
help lower levels of uric acid in your body to prevent or reduce future
episodes of gout attacks:
- Allopurinol is taken as a pill.
- Febuxostat is taken as a pill.
- Pegloticase is given as an intravenous (in the
vein) infusion.
- Probenecid is taken as a pill.
Can I prevent gout?
You can make certain lifestyle changes to
help prevent gout:
- Drink plenty of water to help your kidneys function
better and avoid dehydration.
- Exercise regularly to stay at a healthy weight.
Extra weight increases uric acid in your body and puts more stress on
joints.
Do your best
to limit the purines in your body, since these chemicals can trigger uric acid
buildup. Foods and drinks containing high purine levels include:
- Alcohol.
- Red meat and organ meats (liver, for example).
- Shellfish.
- Gravy.
- Drinks and foods high in fructose (fruit sugar).
- Protein from animal sources. All protein from
animal flesh can potentially lead to elevated uric acid levels.
Certain
medications can lead to elevated uric acid levels. These medications include:
- Diuretics, also known as “water pills.”
- Immunosuppressants or drugs are used to slow the immune
system (standard in organ transplants, for example).
When should I call my healthcare provider about gout symptoms?
If you
experience sudden, intense pain in a joint, call a healthcare provider right
away. If the joint is hot and inflamed, you might have gout or another problem like an infection.
What’s the outlook for people with gout?
Untreated gout can lead to permanent joint damage. The buildup of uric acid in the joints and soft tissue is called tophus. Some people with gout can also develop other health problems, such as severe arthritis, kidney stones, and heart disease. It’s important to discuss your symptoms with a healthcare provider.
How can I manage a gout attack?
When you have a gout attack, you can
manage your symptoms by:
- Avoid alcohol and sweet drinks.
- Drinking plenty of fluids.
- Elevating the joint(s).
- Putting ice on the joint(s).
- Limiting any stress on the joint(s).
What else should I ask my healthcare provider about gout?
Consider
asking your healthcare provider:
- What is causing gout?
- Do I have any joint damage?
- What can I do to prevent future attacks?
- Can any gout medications help me?
- How long will I need to take gout medications?
A gout is a painful form of arthritis. Extra
uric acid in your body creates sharp crystals in the joints, leading to
swelling and extreme tenderness. Gout usually starts in the big toe but can
affect other joints. Gout is a treatable condition, and the uric acid level can
be decreased by medication and lifestyle changes. Talk to your healthcare
provider about medications that can reduce uric acid levels. They can also
discuss changes you can make to your diet and lifestyle to prevent and reduce
gout attacks.
Would your
friends be interested? Share this story!
( Keywords )
Post a Comment